
Borates float on top of the liquor while rock and clay settles to the bottom. After dissolving the ore, the saturated borate solution is pumped into a large settling tank. Sedimentation is used by Rio Tinto Minerals to refine raw ore into refined borates. Methods used to treat suspended solids in mining wastewater include sedimentation and floc blanket clarification and filtration. Sedimentation tanks called 'secondary clarifiers' remove flocs of biological growth created in some methods of secondary treatment including activated sludge, trickling filters and rotating biological contactors.
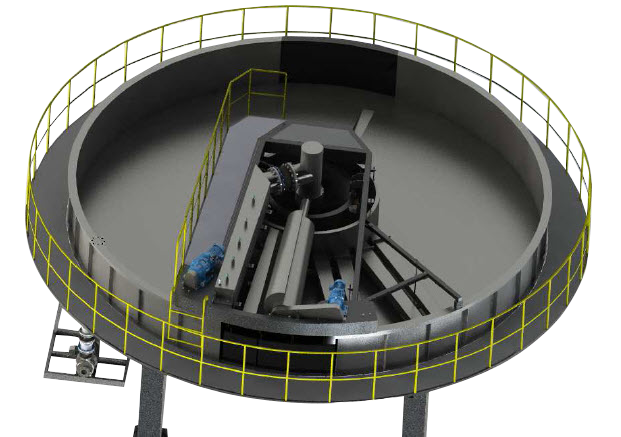

However, coagulation and flocculation can be used for building a compact treatment plant (also called a "package treatment plant"), or for further polishing of the treated water. : 5–9 Because of the large amount of reagent necessary to treat domestic wastewater, preliminary chemical coagulation and flocculation are generally not used, remaining suspended solids being reduced by following stages of the system. Primary clarifiers reduce the content of suspended solids and pollutants embedded in those suspended solids. Primary treatment of sewage is removal of floating and settleable solids through sedimentation. Sedimentation tanks have been used to treat wastewater for millennia. Clarified water then proceeds through several more steps before being sent for storage and use. The particles then form a bottom layer of sludge requiring regular removal and disposal. The clarifier works by permitting the heavier and larger particles to settle to the bottom of the clarifier. Isolating the particle components first using these processes may reduce the volume of downstream water treatment processes like filtration.ĭrinking water, water being purified for human consumption, is treated with flocculation reagents, then sent to the clarifier where removal of the flocculated coagulate occurs producing clarified water. This allows the separation of the solids in the clarifier to occur more efficiently and easily, aiding in the conservation of energy. These reagents cause finely suspended particles to clump together and form larger and denser particles, called flocs, that settle more quickly and stably. Concentrated impurities, discharged from the bottom of the tank, are known as sludge, while the particles that float to the surface of the liquid are called scum.Īpplications Pretreatment īefore the water enters the clarifier, coagulation and flocculation reagents, such as polyelectrolytes and ferric sulfate, can be added. Inside the clarifier, solid contaminants will settle down to the bottom of the tank where it is collected by a scraper mechanism. A clarifier is generally used to remove solid particulates or suspended solids from liquid for clarification and/or thickening. As the skimmer slowly rotates around the clarifier, skimmed floating material is pushed into the trap visible above the fenced enclosure at the lower left.Ĭlarifiers are settling tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by sedimentation. Circular clarifier with surface skimmer visible in the lower right.


They appear to have a floating cover to reduce the odor because the plant is very close to a residential area. Three wastewater/sewage clarifiers at the ʻAikahi wastewater treatment plant in Hawaii. For a description of simpler settling ponds without solids removal machinery, see Settling basin. This article is about concrete and metal sedimentation tanks including continuous mechanized removal of solids.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
